A2. Location
Greece is located on the Mediterranean Sea which sits to the south. The Aegean Sea is on the east side, between Greece's mainland and Asia Minor. The country is composed of a mainland and various islands.
A1. Time Period: 3,000 B.C. - 323 B.C. |
|
|
|
A2. Location |
|
|
Greece is located on the Mediterranean Sea which sits to the south. The Aegean Sea is on the east side, between Greece's mainland and Asia Minor. The country is composed of a mainland and various islands. |
|
A2. General Comments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B. Social |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C. Economic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D. Commerce |
|
|
|
|
|
|
E. Religion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
F. Literature and Art |
|
|
|
G. Intellectual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
H. Wars |
|
| 1.
Persian War, 479 - 439 B.C. 2. Peloponnesian War, 431 - 404 BC Athens vs. Sparta 3. Rise of Macedonia and Alexander the Great 404 - 323 B.C. 4. Hellenistic Age, 323 BC to 31 BC |
|
|
|
|
I. Summary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
II Costume Overview
A. Motifs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
B. Materials |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C. Silhouette |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D. Other Information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
III Costume Items
A. Garments |
|
|
Chiton
|
|
|
fibula
|
|
|
chlamys
|
|
|
girdle
|
|
|
himation
|
|
|
peplos
|
|
B. Headwear |
|
|
|
|
|
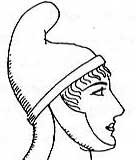
Phrygian
Cap
|
 |
|
tholia |
|
|
tiara/stephane
|
|
|
Jewelry:
necklaces, earrings, rings, decorative pins (fibulae) and brooches
|
|
|
hair
|
 |
C. Footwear |
|
|
Buskin |
|
|
sandals |
|
|
|
|
IV What Am I?
Current and not so current fashion |
|